| [1] 裴壮敏.玻璃离子水门汀用于口腔正畸的疗效观察[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(26):306-307.
[2] 廖伟,周年苟,扈祚文,等.不同口腔修复材料生物相容性及3种材料充填恒磨牙邻面龋的临床验[J].中国组织工程实验与临床康复,2011,15(8):1467-1470.
[3] Balamungan A, Baiossier G, Lanrent-Maquifi D, et al. An in vitro biological and antibacterial study oll a sollel derived silver-incerporated biogless system. Dent Mater. 2008; 24(10):1343-1351.
[4] Arita K, Lucas ME, Nishino M. The effect of adding hydroxyapatite on the flexural strength of glass ionomer cement. Dent Mater. 2003;22(2):126-136.
[5] 赵昱,苏葆辉,冉均国,等.乙酸处理对玻璃离子水门汀性能的影响[J].硅酸盐通报,2013,32(2):304-308.
[6] Smith DC. Development of glass-ionomer cement systems. Biomaterials. 1998;19:467-478.
[7] Dowling AH, Stamboulis A, Fleming GJ. The influence of montmorillonite clay reinforcement on the performance of a glass ionomer restorative. J Dent. 2006;34:802-810.
[8] Nakajima N, Watkins JH, Arita K, et al. Mechanical properties of glass ionomers under static and dynamic loading. Dent Mater. 1996;12:30-37.
[9] 刘莉霞,陈琳.不同类型玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放行为与溶解性[J].中国组织工程实验,2014,18(16):2480-2486.
[10] 陈娜,刘聪,李行懿.不同类型玻璃离子水门汀氟释放能力的比较分析[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(10):64-66.
[11] 董波,刘文斌,李晶晶,等.纳米纤维素晶须对新型玻璃离子水门汀增韧作用的影响[J].中国体视学与图像分析,2013,18(4):361- 366.
[12] 董波,徐志媛,刘文斌,等.纳米纤维素晶须对玻璃离子水门汀的性能影响[J].中国体视学与图像分析,2013,18(1):23-28.
[13] 冯瑶,冯思聪,王建平,等.玻璃离子水门汀加入改良纳米羟基磷灰石后的性能[J].中国组织工程实验,2013,17(42):7382- 7388.
[14] Moshaverinia A, Ansari S, Moshaverinia M, et al. Effects of incorporation of hydroxyapatite and fluoroapatite nanobioceramics into conventional glass ionomer cements (GIC). Acta Biomaterialia, 2008;4:432-440.
[15] Prentice LH, Tyas MJ, Burrow MF. The effect of ytterbium fluoride and barium sulphate nano particles on the reactivity and strength of a glass-ionomer cement. Dent Mater. 2006; 22:746-751.
[16] Moshaverinia A, Ansari S, Movasaghi Z, et al. Modification of conventional glass-ionomer cements with N-vinylpyrrolidone containing polyacids, nano-hydroxy and fluoroapatite to improve mechanical properties. Dent Mater. 2008;24: 1381-1390.
[17] Tllrklln LS, Turkan M. Long-term antibacterial effects and physical properties of a chlorhexidine-containing glass ionomer cement. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2008;20(1):29-45.
[18] Xia Y, Zhang F, Xie H, et al. Nano particle-reinforced resinbased dental composites. J Dent. 2008;36:450-455.
[19] 尹雯娟,叶慧铭,侯雅蓉,等.玻璃离子水门汀调拌过程中常见问题分析[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(22):3784-3784.
[20] 曹院琴,李永祥.3种玻璃离子水门汀氟释放能力的体外实验[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2013,11(2):116-118.
[21] 张海英,吕松,侯本祥.四种玻璃离子充填材料释氟性与溶解性的实验[J].北京口腔医学,2011,19(5):260-262.
[22] Al Zraikat H, Palamara JE, Messer HH, et al. The incorporation of casein phosphopeptideamorphous calcium phosphate into a glass ionomer cement. Dent Mater. 2011; 27:235-243.
[23] Kao EC, Culbertson BM, Xie D. Preparation of glass ionomer cement using N-acryloyl-substituted amino acid monomers-evaluation of physical properties. Dent Mater. 1996;12:44-51.
[24] Tanumiharja M, Burrow MF, Tyas MJ. Microtensile bond strengths of glass ionomer (polyalkenoate) cements to dentine using four conditioners. J Dent. 2000;28:361-366.
[25] Tsuang YH, Sun JS, Huang YC, et al. Studies of photokilling of bacteria using titanium dioxide nano particles. Artificial Organs. 2008;32:167-174.
[26] Chan WD, Yang L, Wang W, et al. Fluoride release from dental cements and composites: a mechanistic study. Dent Mater,2006;22(4):366-373.
[27] Verbeeck RM, deMoor RJ, Van Even DF, et al. The short-term fluoride release of a hand-mixed vs. cap sulated system of a restorative glass-ionomer cement. J Dent Res. 1993;72: 577-581.
[28] Choi JY, Lee HH, Kim HW. Bioactive sol-gel glass added ionomer cement for the regeneration of tooth structure. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(10):3287-3294.
[29] Vermeersch G, Leloup G, Delmee M, et al. Antibacterial activity of glass-ionomer cements, compomers and resin composites: relationship between acidity and material setting phase. J Oral Rehabilit. 2005;32:368-374.
[30] Nychka JA, Li D, Alexander B. In vitro bioactivity of 45S5 bioactive glass as a function of indentation load. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2008;1(3):243-251.
[31] Butler KS, Casey BJ, Garbocauskas GV, et al. Assessment of titanium dioxide nanoparticle effects in bacteria: Association, uptake, mutagenicity, co-mutagenicity and DNA repair inhibition. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2014.
[32] Makumire S, Chakravadhanula VS, Köllisch G, et al. Immunomodulatory activity of zinc peroxide (ZnO?) and titanium dioxide (TiO?) nanoparticles and their effects on DNA and protein integrity. Toxicol Lett. 2014;227(1):56-64.
[33] Dasari TP, Hwang HM. Effect of humic acids and sunlight on the cytotoxicity of engineered zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles to a river bacterial assemblage. J Environ Sci (China). 2013;25(9):1925-1935.
[34] Minetto D, Libralato G, Volpi Ghirardini A. Ecotoxicity of engineered TiO2 nanoparticles to saltwater organisms: an overview. Environ Int. 2014;66:18-27.
[35] Kedziora A, Gerasymchuk Y, Sroka E, et al. Use of the materials based on partially reduced graphene-oxide with silver nanoparticle as bacteriostatic and bactericidal agent. Polim Med. 2013;43(3):129-134.
[36] Binh CT, Tong T, Gaillard JF, et al. Common freshwater bacteria vary in their responses to short-term exposure to nano-TiO2. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2014;33(2):317-327.
[37] Gartiser S, Flach F, Nickel C, et al. Behavior of nanoscale titanium dioxide in laboratory wastewater treatment plants according to OECD 303 A. Chemosphere. 2014;104:197-204.
[38] Hammond SA, Carew AC, Helbing CC. Evaluation of the effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cultured Rana catesbeiana tailfin tissue. Front Genet. 2013;4:251.
[39] Zhou L, Zhang Z, Xia S, et al. Effects of suspended titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cake layer formation in submerged membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol. 2014;152:101-106.
[40] Shokri M, Jodat A, Modirshahla N, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of chloramphenicol in an aqueous suspension of silver-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ Technol. 2013; 34(9-12):1161-1166.
[41] Patil MA, Parikh PA. Investigation on likely effects of Ag, TiO2, and ZnO nanoparticles on sewage treatment. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014;92(1):109-114.
[42] Zhang J, Liu Y, Li Q, et al. Antifungal activity and mechanism of palladium-modified nitrogen-doped titanium oxide photocatalyst on agricultural pathogenic fungi Fusarium graminearum. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(21): 10953-10959.
[43] Frazier TP, Burklew CE, Zhang B. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles affect the growth and microRNA expression of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Funct Integr Genomics. 2014; 14(1):75-83.
[44] Vatansever F, Ferraresi C, de Sousa MV, et al. Can biowarfare agents be defeated with light? Virulence. 2013; 4(8):796-825.
[45] Shah N, Ul-Islam M, Khattak WA, et al. Overview of bacterial cellulose composites: a multipurpose advanced material. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;98(2):1585-1598. |
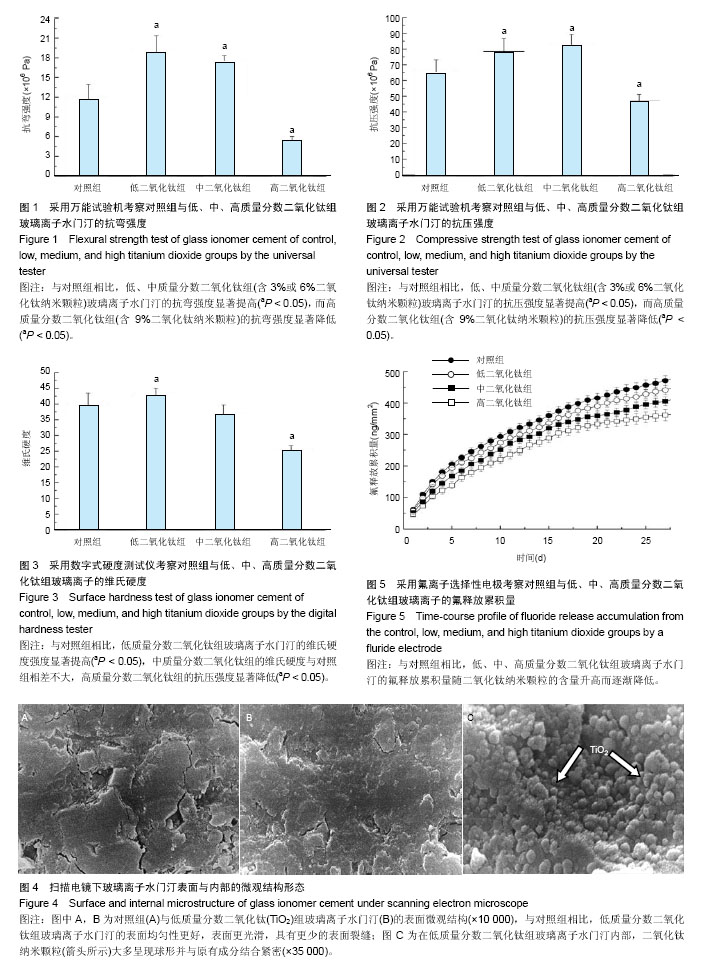
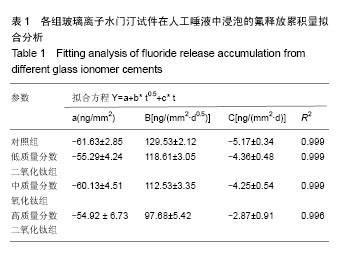
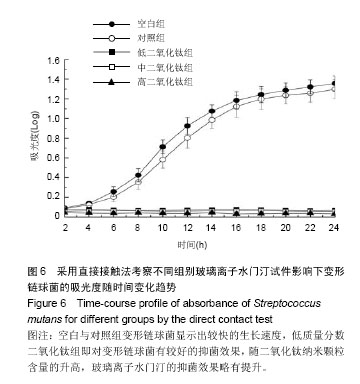
.jpg)